Now Reading: Comprehensive Guide to Sequence Diagrams: From Theory to Practice with Visual Paradigm & AI
-
01
Comprehensive Guide to Sequence Diagrams: From Theory to Practice with Visual Paradigm & AI
Comprehensive Guide to Sequence Diagrams: From Theory to Practice with Visual Paradigm & AI
🌟 Introduction
Sequence diagrams are one of the most powerful UML (Unified Modeling Language) tools used in software engineering to visualize the dynamic behavior of a system—specifically, how objects interact over time in a particular scenario.
The example you provided—a sequence diagram for booking a flight online—is a perfect illustration of how complex business logic can be broken down into clear, step-by-step interactions between system components.
This guide dives deep into:
-
What sequence diagrams are
-
Key concepts and notation
-
Best practices, guidelines, and tips/tricks
-
How to use Visual Paradigm’s All-in-One Platform with AI assistance to streamline creation and maintenance
📌 Part 1: What Is a Sequence Diagram?
A sequence diagram is a type of interaction diagram that shows how objects communicate in a specific scenario, emphasizing the order of messages over time.

It’s ideal for modeling:
-
User workflows (e.g., booking a flight)
-
System integrations (e.g., payment processing)
-
Real-time or asynchronous interactions
✅ Think of it like a timeline of events where each participant (actor or system) is a vertical lifeline, and horizontal arrows represent messages sent between them.
🧩 Part 2: Key Concepts & Elements
Let’s break down the core elements used in your flight booking diagram:
1. Actors
-
Represent external entities interacting with the system.
-
Example:
User(USR) in your diagram. -
Drawn as stick figures or labeled rectangles.
-
Often placed on the far left.
💡 Tip: Use
actorkeyword in PlantUML to define them.
actor "User" as USR
2. Participants (Objects/Components)
-
Internal system components or services.
-
Example:
Flight Search Service,Booking Service,Payment Service,Flight Database.
✅ These are rectangles with rounded corners or boxes in UML.
participant "Flight Search Service" as FSS
3. Lifelines (Vertical Dashed Lines)
-
Vertical lines extending from each participant.
-
Represent the duration of an object’s existence during the interaction.
-
The longer the line, the longer the object is “active”.
🔁 Lifelines are automatically drawn in most tools (including Visual Paradigm).
4. Activation Bars (Rectangles on Lifelines)
-
Horizontal rectangles on lifelines indicating when an object is actively performing work.
-
Represent method execution, processing, or waiting.
activate FSS
✅
activatestarts the activation bar;deactivateends it.
5. Messages (Arrows)
-
Arrows between lifelines showing communication.
-
Synchronous (solid arrow): Wait for response (e.g.,
FSS -> FD: Get available flights) -
Asynchronous (open arrow): Non-blocking call (e.g.,
FSS -> BS: Confirm booking)
⚠️ In PlantUML, all arrows are assumed synchronous unless specified otherwise.
6. Alternatives (alt, else, else if)
-
Conditional logic in sequence diagrams.
-
altmeans “if condition is true” -
elsehandles the alternative case -
else ifcan be used for multiple conditions
alt Flights found
FD --> FSS: Return flight options
else No flights available
FD --> FSS: No flights found
else User cancels booking
USR -> BS: Cancel booking
end
✅ Great for modeling error handling, user decisions, and branching logic.
7. Loops (loop)
-
Repeated actions.
-
Example:
loop While payment pending -
Useful for retry mechanisms or batch processing.
8. Fragments (opt, break, critical, par, etc.)
-
opt: Optional (if condition met) -
break: Interrupt or exception handling -
par: Parallel execution
These help structure complex interactions clearly.
🛠 Part 3: Guidelines for Writing Effective Sequence Diagrams
| Principle | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| 1. Focus on One Use Case | Don’t try to model everything in one diagram. Keep it scoped. |
| 2. Order Matters | Draw interactions in chronological order from top to bottom. |
| 3. Use Clear Labels | Avoid vague messages like “send data.” Be specific: “Send user ID to authentication service.” |
| 4. Limit Participants | More than 6–7 participants can make the diagram cluttered. Split into multiple diagrams if needed. |
| 5. Use Activation Bars Wisely | Only activate when the object is doing work. Avoid long activations unless necessary. |
| 6. Group Related Logic | Use alt, loop, par to group logic and improve readability. |
| 7. Prioritize Clarity Over Completeness | A clean, understandable diagram is better than a dense, over-annotated one. |
💡 Part 4: Tips & Tricks for Better Diagrams
| Tip | Why It Helps |
|---|---|
| ✅ Start with the user journey | Begin with the actor and trace their interaction through the system. |
| ✅ Use consistent naming | Use PascalCase or snake_case consistently across all participants. |
| ✅ Group related services | E.g., group Booking, Payment, Notification under “Reservation Engine” if they’re tightly coupled. |
| ✅ Use color coding | In tools like Visual Paradigm, assign colors to service types (e.g., red for payment, blue for search). |
| ✅ Use comments | Add note right of or note left of to explain complex logic. |
| ✅ Keep messages concise | Use verb + object format: Request flight data, Confirm seat reservation |
🚀 Part 5: Using Visual Paradigm’s All-in-One Platform + AI to Streamline Sequence Diagrams
Visual Paradigm (VP) is a full-stack UML/Software Modeling tool that integrates AI-powered features, making diagram creation faster, smarter, and more collaborative.
Let’s walk through how you can use it with AI to create and enhance your flight booking sequence diagram.
✅ Step 1: Start with a Template or AI Prompt
Instead of drawing from scratch:
-
Open Visual Paradigm Online (or desktop).
-
Go to Create > UML > Sequence Diagram.
-
Use the AI Assistant (powered by LLMs like GPT or custom models).
👉 Prompt Example:
“Generate a sequence diagram for a flight booking system where a user searches flights, the system checks availability, confirms a booking, processes payment, and reserves a seat. Include error handling for no flights found and user cancellation.”
✅ Result: VP generates a clean, structured sequence diagram in seconds.
✅ Step 2: Auto-Generate from Natural Language (AI-Powered)
-
Paste your PlantUML code (like the one you provided) into VP’s Text to Diagram feature.
@startuml skinparam sequenceParticipant underline skinparam { ' Overall style FontSize 14 ' Colors ArrowColor #4A4A4A ArrowFontColor #4A4A4A BackgroundColor #FFFFFF BorderColor #DEDEDE FontColor #333333 ' Participant styling Participant { BorderColor #0077B6 BackgroundColor #F0F8FF FontColor #005691 } ' Actor styling Actor { BorderColor #6A057F BackgroundColor #F5EEF8 FontColor #510363 } ' Sequence specific Sequence { ArrowThickness 2 LifeLineBorderColor #444444 LifeLineBackgroundColor #F7F7F7 BoxBorderColor #AAAAAA BoxBackgroundColor #FFFFFF BoxFontColor #333333 } } actor "User" as USR participant "Flight Search Service" as FSS participant "Booking Service" as BS participant "Payment Service" as PS participant "Flight Database" as FD USR -> FSS: Search flights activate USR activate FSS FSS -> FD: Get available flights activate FD alt Flights found FD --> FSS: Return flight options deactivate FD FSS -> USR: Show flight results FSS -> BS: Confirm booking activate BS BS -> FD: Reserve seat activate FD FD --> BS: Seat reserved deactivate FD BS -> PS: Process payment activate PS PS -> BS: Payment successful activate BS BS --> USR: Booking confirmed deactivate BS deactivate PS deactivate FSS deactivate USR else No flights available FD --> FSS: No flights found deactivate FD FSS --> USR: No flights match criteria deactivate FSS deactivate USR else User cancels booking USR -> BS: Cancel booking activate BS BS -> FD: Release seat activate FD FD --> BS: Seat released deactivate FD BS --> USR: Booking cancelled deactivate BS deactivate USR end @enduml -
VP parses the code and renders the diagram instantly
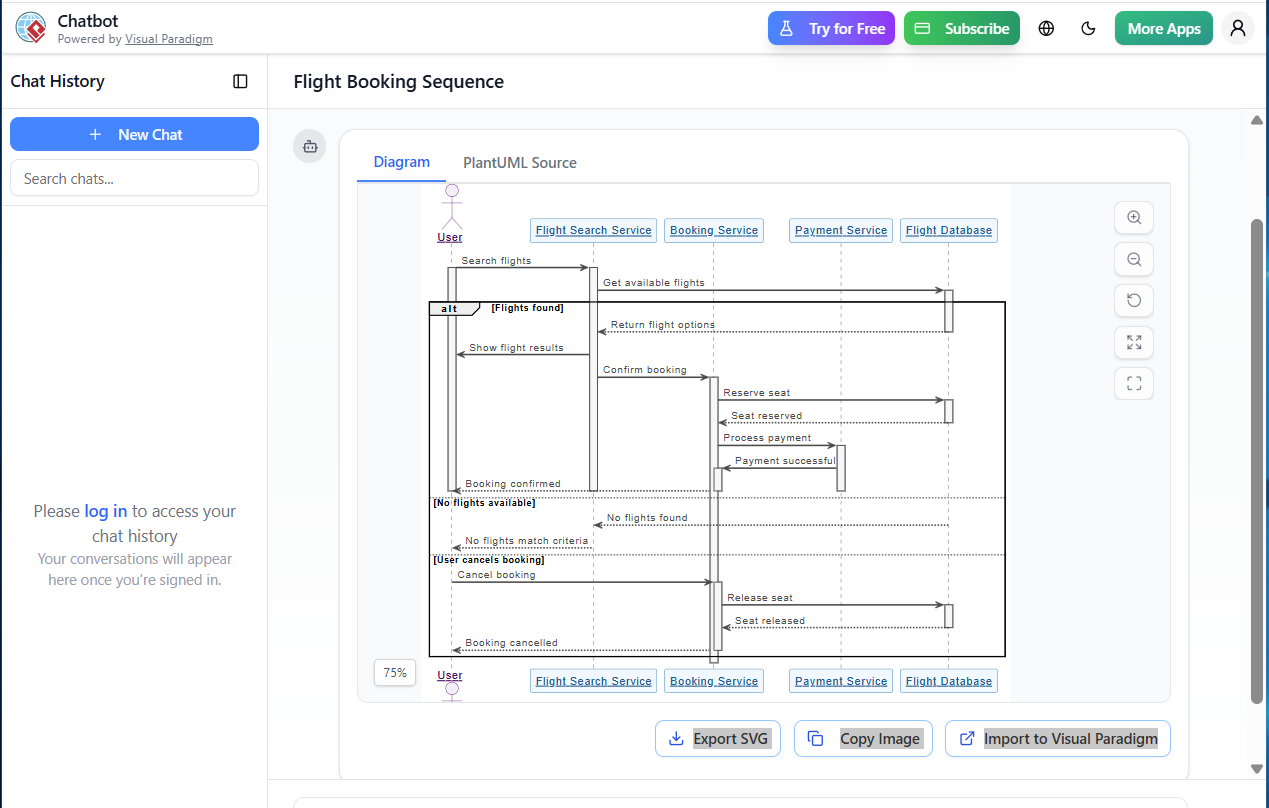
-
Automatically adds lifelines, activation bars, and message labels.
🔄 No more syntax errors or manual layout adjustments.
✅ Step 3: Enhance with AI Suggestions
After generating the diagram:
-
Right-click on the diagram → AI Assistant → Improve Diagram
-
AI suggests:
-
Better message wording
-
Missing error cases
-
Better participant grouping
-
Suggested use of
loop,alt, orpar
-
Example: AI might suggest adding a
loopfor retrying payment or abreakfor timeout.
✅ Step 4: Collaborate & Document
-
Share the diagram via link or embed in docs.
-
Add notes, requirements, test cases, or API specs directly in the model.
-
Link to use case diagrams, activity diagrams, or class diagrams for full traceability.
📌 This creates a living documentation system.
✅ Step 5: Export & Integrate
-
Export as:
-
PNG/SVG (for reports)
-
PDF (for documentation)
-
HTML (for web integration)
-
🔄 You can even reverse-engineer a sequence diagram from code using VP’s Code to Diagram feature.
🎯 Real-World Benefits of Using Visual Paradigm + AI
| Benefit | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Speeds up modeling | AI generates diagrams from text in seconds |
| Reduces errors | AI checks consistency, naming, logic flow |
| Improves collaboration | Teams can discuss and refine diagrams in real time |
| Enables automation | Link diagrams to code, tests, and documentation |
| Scales across projects | Reuse templates and AI rules across teams |
📋 Summary: Your Flight Booking Sequence Diagram – Final Checklist
| Element | Done? |
|---|---|
| Actor defined? | ✅ |
| Participants clearly named? | ✅ |
| Lifelines and activation bars used? | ✅ |
| Messages are clear and ordered? | ✅ |
alt, else, deactivate used correctly? |
✅ |
| Diagram is readable (not too many participants)? | ✅ |
| AI-enhanced for clarity & completeness? | ✅ |
📚 Bonus: Recommended Resources
-
PlantUML Official Docs: https://plantuml.com
-
Visual Paradigm UML Guide: https://www.visual-paradigm.com/guide/uml/
-
AI-Powered Modeling Tutorials: Search “Visual Paradigm AI diagram generator” on YouTube or their blog.
🏁 Final Thoughts
Sequence diagrams are not just for developers—they are powerful communication tools for:
-
Product managers
-
QA engineers
-
Business analysts
-
DevOps teams
With Visual Paradigm’s All-in-One Platform + AI, you can:
-
Create diagrams faster than ever
-
Maintain consistency across teams
-
Turn ideas into models with minimal effort
-
Integrate with your entire SDLC pipeline
🎯 Pro Tip: Treat your sequence diagrams as living artifacts—update them as the system evolves. Use AI to keep them in sync with code and requirements.
📣 Ready to Get Started?
👉 Try Visual Paradigm Free: https://www.visual-paradigm.com
Use the AI Diagram Generator and paste your PlantUML code or describe your use case. Watch your flight booking diagram come to life in seconds—with smart suggestions and clean visuals.
🚀 Now you’re not just drawing diagrams—you’re modeling smarter.
-
Comprehensive Guide to Sequence Diagrams in Software Design: This detailed handbook section explains the purpose, structure, and best practices for using sequence diagrams to model dynamic system behavior.
-
What Is a Sequence Diagram? – A UML Guide: an introductory guide explaining the role of sequence diagrams in visualizing object interactions over time.
-
Animating Sequence Diagrams in Visual Paradigm – Tutorial: This tutorial provides instructions on creating dynamic, animated sequence diagrams to visualize software workflows effectively.
-
Visual Paradigm – AI-Powered UML Sequence Diagrams: This resource demonstrates how the platform’s AI engine enables users to generate professional UML sequence diagrams instantly from text.
-
AI-Powered Sequence Diagram Refinement in Visual Paradigm: This article explores how AI tools can transform use-case descriptions into precise sequence diagrams with minimal manual effort.
-
Mastering Sequence Diagrams with Visual Paradigm: AI Chatbot Tutorial: A beginner-friendly tutorial that uses a real-world e-commerce chatbot use case to teach sequence diagram modeling.
-
How to Model MVC with UML Sequence Diagram | Visual Paradigm: This guide teaches users how to visualize interactions between Model, View, and Controller components to improve architectural clarity.
-
Visual Paradigm: Separate Sequence Diagrams for Main and Exceptional Flows: This technical post explains how to model both main and alternative/exceptional flows using separate diagrams to maintain model readability.
-
PlantUML Sequence Diagram Generator | Visual Builder Tool: An overview of a visual generator that allows users to define participants and messages using a step-by-step wizard to create PlantUML-based sequence diagrams.
-
The Power of Sequence Diagrams in Team Collaboration – Viz Tools: An article discussing why sequence diagrams are essential for team communication and how Visual Paradigm serves as a robust tool for this purpose.












