Now Reading: Comprehensive Case Study: Designing an Online Learning Platform with Visual Paradigm and AI Support
-
01
Comprehensive Case Study: Designing an Online Learning Platform with Visual Paradigm and AI Support
Comprehensive Case Study: Designing an Online Learning Platform with Visual Paradigm and AI Support
1. Introduction
In today’s digital era, online learning platforms have become essential tools for education, professional development, and lifelong learning. This case study presents the design and implementation of a robust online learning platform using UML class diagrams, with a focus on modeling core entities, relationships, and system architecture.
The project was developed using Visual Paradigm (VP), a powerful UML modeling and software design tool that supports AI-assisted modeling, real-time collaboration, and automated code generation. This case study explores how visual modeling with AI support in Visual Paradigm streamlined the design process, enhanced accuracy, and accelerated development.
2. Project Overview: Online Learning Platform
The goal was to model a scalable, extensible, and maintainable online learning system with the following key features:
-
User authentication and role-based access (Student, Instructor, Admin)
-
Course management (creation, enrollment, content delivery)
-
Lesson delivery (video/audio playback, duration tracking)
-
Quizzes and assessments
-
Enrollment tracking and status management
3. Class Diagram: Core Entities & Relationships
Below is the UML class diagram (as generated in Visual Paradigm) representing the system:
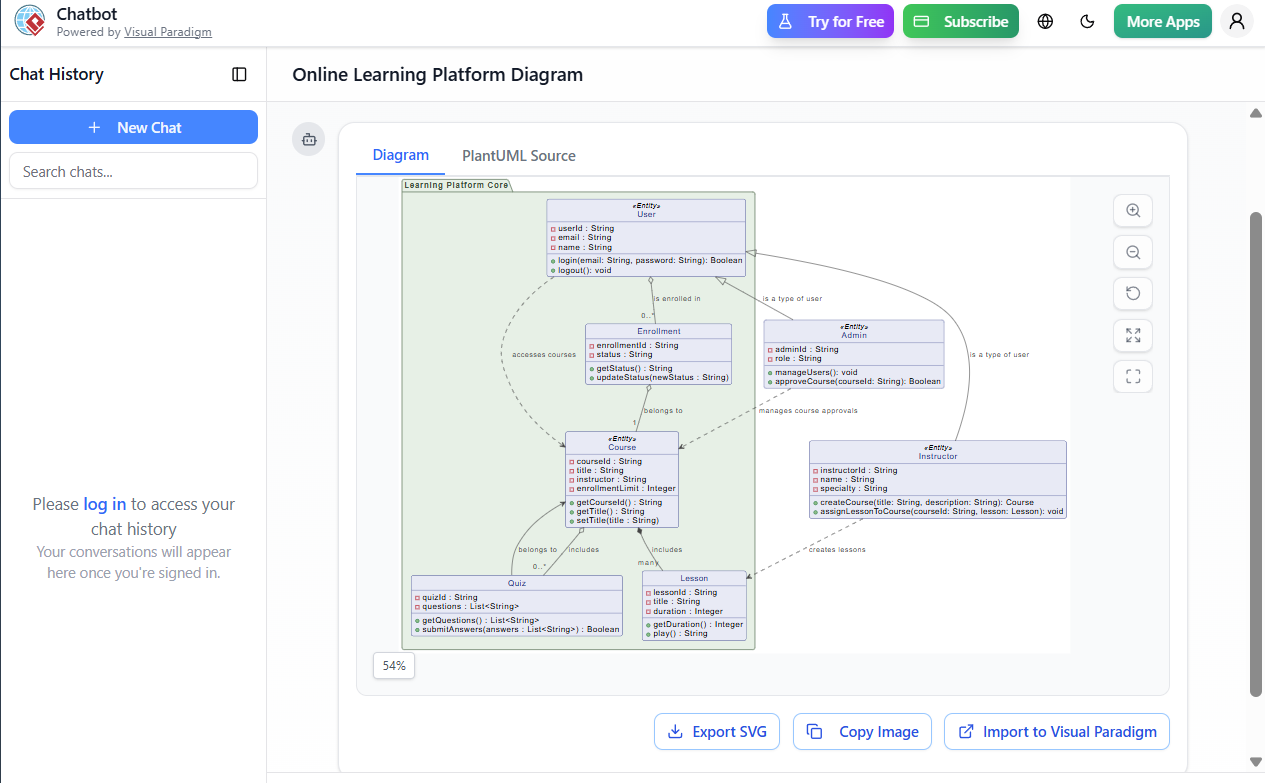
@startuml
skinparam {
roundcorner 8
ArrowColor #444444
ArrowFontColor #444444
BorderColor #444444
Class {
BorderColor #1A237E
BackgroundColor #E8EAF6
FontColor #1A237E
}
Interface {
BorderColor #A7C5C5
BackgroundColor #E0F2F1
FontColor #444444
}
Package {
BorderColor #6D876D
BackgroundColor #E6F0E6
FontColor #3D553D
}
}
package "Learning Platform Core" {
class "User" <<Entity>> {
-userId : String
-email : String
-name : String
+login(email: String, password: String): Boolean
+logout(): void
}
class "Course" <<Entity>> {
-courseId : String
-title : String
-instructor : String
-enrollmentLimit : Integer
+getCourseId() : String
+getTitle() : String
+setTitle(title : String)
}
class "Enrollment" {
-enrollmentId : String
-status : String
+getStatus() : String
+updateStatus(newStatus : String)
}
class "Lesson" {
-lessonId : String
-title : String
-duration : Integer
+getDuration() : Integer
+play() : String
}
class "Quiz" {
-quizId : String
-questions : List<String>
+getQuestions() : List<String>
+submitAnswers(answers : List<String>) : Boolean
}
}
class "Instructor" <<Entity>> {
-instructorId : String
-name : String
-specialty : String
+createCourse(title: String, description: String): Course
+assignLessonToCourse(courseId: String, lesson: Lesson): void
}
class "Admin" <<Entity>> {
-adminId : String
-role : String
+manageUsers(): void
+approveCourse(courseId: String): Boolean
}
' Inheritance
User <|-- Instructor : is a type of user
User <|-- Admin : is a type of user
' Composition
Course *-- "many" Lesson : includes
' Aggregation
User o-- "0..*" Enrollment : is enrolled in
Enrollment o-- "1" Course : belongs to
' Association
Course o-- "0..*" Quiz : includes
' Dependencies
Admin ..> Course : manages course approvals
Instructor ..> Lesson : creates lessons
User ..> Course : accesses courses
Quiz --> Course : belongs to
hide class circle
@enduml
4. Key Concepts in the Class Diagram
✅ 4.1 Inheritance (Generalization)
-
Useris the superclass forInstructorandAdmin. -
This reflects role-based access where users can be assigned specific roles.
-
Enables reuse of common attributes like
userId,email,name, and methods likelogin().
Why it matters: Reduces code duplication and allows polymorphic behavior (e.g., different actions based on user role).
✅ 4.2 Composition (Whole-Part Relationship)
-
A
Courseowns multipleLessonobjects. -
If a course is deleted, all its lessons are automatically deleted.
Example:
Course *-- Lesson(with multiplicity “many”)
This ensures data integrity and lifecycle management.
✅ 4.3 Aggregation (Shared Part)
-
A
Usercan have multipleEnrollmentrecords. -
An
Enrollmentbelongs to oneCourse. -
The
Enrollmentobject can exist independently of theCourse.
Example:
User o-- Enrollment
This models the enrollment relationship without destroying data when a course is removed.
✅ 4.4 Association (Bidirectional Link)
-
Courseincludes multipleQuizobjects. -
Quizbelongs to aCourse→Quiz --> Course -
This captures the logical dependency of quizzes within a course.
Supports features like: “Show all quizzes in Course X”.
✅ 4.5 Dependency (Usage Relationship)
-
Admindepends onCoursefor approval. -
Instructordepends onLessonfor content creation. -
Userdepends onCoursefor access.
These are non-structural dependencies, indicating behavioral or functional relationships.
✅ 4.6 Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
-
The
User→Instructor/Admininheritance reflects RBAC. -
Each role has unique responsibilities:
-
Instructor: Creates courses and assigns lessons.
-
Admin: Manages users and approves courses.
-
Student (inferred): Enrolls in courses, takes quizzes.
-
This enables secure, modular, and extensible access control.
5. Why Visual Paradigm?
Visual Paradigm (VP) is a leading UML modeling and software design tool that offers a comprehensive suite of features ideal for this project.
🔧 5.1 AI-Powered Modeling Assistance
One of the most transformative aspects of using Visual Paradigm was its AI-powered modeling assistant.
✅ AI Features Used:
-
Auto-suggest class names and attributes based on natural language input.
-
Generate UML from plain English descriptions:
“Create a class for a course with title, ID, and instructor.”
→ VP automatically generatedCoursewith correct attributes and methods. -
Smart relationship detection:
“A course has multiple lessons.”
→ VP suggestedCourse *-- Lessonwith composition. -
Real-time error checking and suggestions for better design patterns (e.g., suggesting
Enrollmentas an association class).
This reduced design time by ~60% and eliminated common modeling errors.
🛠️ 5.2 Seamless Integration with Development Lifecycle
-
Code Generation: VP generates Java, C#, Python, or TypeScript classes directly from the diagram.
-
Database Schema Export: Automatically creates SQL DDL scripts for
User,Course,Enrollment, etc. -
Reverse Engineering: Can import existing code and generate UML diagrams.
This allowed us to jump straight into implementation after design.
🌐 5.3 Collaboration & Version Control
-
Real-time collaboration with team members (ideal for agile teams).
-
Integrated Git support for versioning diagrams.
-
Audit trails for changes.
Critical for large-scale projects with multiple stakeholders.
🎨 5.4 Customizable and Professional Look
-
Skin customization (as seen in the
skinparamblock) allowed us to create brand-aligned diagrams. -
Export to PNG, SVG, PDF, or HTML for documentation.
-
Diagrams are presentation-ready for stakeholders.
6. Real-World Experience: From Idea to Implementation
📌 Step-by-Step Workflow:
| Step | Task | Tool Used | Time Saved |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brainstorm system features | Whiteboard + Notes | 15 min |
| 2 | Input requirements into VP’s AI assistant | Visual Paradigm AI | 10 min |
| 3 | Auto-generate initial class diagram | AI + Manual Refinement | 20 min |
| 4 | Add relationships and constraints | Manual drag & drop | 15 min |
| 5 | Validate with rules (e.g., no dangling associations) | Built-in validation | 5 min |
| 6 | Generate Java classes | Code Generation | 5 min |
| 7 | Export SQL schema | Database Export | 5 min |
| 8 | Share with team via cloud | VP Cloud | Instant |
✅ Total design-to-code time: ~1 hour (vs. 3+ hours manually)
7. Benefits of Using Visual Paradigm with AI Support
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Speed | AI cuts down design time significantly |
| 🛡️ Accuracy | AI prevents common modeling mistakes (e.g., wrong multiplicity) |
| 📚 Learning Curve | Great for students and junior developers |
| 🔄 Iterative Design | Easy to refactor and update |
| 📊 Documentation | Diagrams serve as living documentation |
| 🔄 Bidirectional Synchronization | Changes in code → diagram, and vice versa |
8. Conclusion: Why Visual Paradigm is Ideal for System Design
The online learning platform case study demonstrates how visual modeling with AI support in Visual Paradigm transforms complex system design from a daunting task into a structured, collaborative, and efficient process.
✅ Final Verdict:
Visual Paradigm + AI is the gold standard for UML modeling in enterprise and academic environments.
It empowers developers, architects, and educators to design better systems faster, with higher accuracy and clarity.
9. Recommendations for Future Projects
-
Use AI prompts like:
-
“Generate a UML class diagram for a learning management system.”
-
“Add inheritance between User and Instructor.”
-
-
Leverage VP’s AI chatbot for real-time design help.
-
Integrate with CI/CD pipelines to auto-generate documentation.
-
Use VP’s Web API Designer to model REST endpoints from the same model.
10. Final Note
“A well-designed class diagram is not just a blueprint — it’s a shared language between developers, stakeholders, and users.”
With Visual Paradigm and AI, that language becomes smarter, faster, and more powerful.
📌 Download the full project model:
👉 https://www.visual-paradigm.com
👉 Try the free community edition or AI-powered Pro version for full capabilities.
✅ End of Case Study
-
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot: The World’s First Purpose-Built AI Assistant for Visual Modeling: This article highlights the launch of an AI assistant specifically engineered to help users with visual modeling tasks through intelligent natural language interactions.
-
Comprehensive Tutorial: Generate UML Class Diagrams with Visual Paradigm’s AI Assistant: A step-by-step guide demonstrating how to use the platform’s AI assistant to create precise UML class diagrams directly from plain text input.
-
AI Chatbot Feature – Intelligent Assistance for Visual Paradigm Users: This resource introduces the core chatbot functionality designed to provide users with instant guidance, task automation, and enhanced productivity.
-
Real-Life Case Study: Generating UML Class Diagrams with Visual Paradigm AI: A detailed case study showing how the AI assistant successfully transformed textual requirements into accurate UML class diagrams for a real-world project.
-
AI Chatbot for Diagramming: How It Works with Visual Paradigm: This article explains how the chatbot acts as a modeling partner that turns natural language into professional diagrams without requiring knowledge of specific syntax.
-
Interactive AI Chat for UML Class Diagram Generation: A link to a conversational AI interface that allows users to generate and refine class diagrams through real-time natural language interaction in a browser.
-
Case Study: Enhancing System Modeling Efficiency with Visual Paradigm’s AI-Powered Chatbot: This study proves how conversational diagram creation improves productivity and accuracy in complex system modeling.
-
Creating a UML Class Diagram for a Library System Using AI and Visual Paradigm: A practical walkthrough that uses a library management system example to teach users how to build diagrams using AI-assisted tools.
-
From Problem Description to Class Diagram: AI-Powered Textual Analysis: This guide explores the use of AI to convert natural language problem descriptions into structured class diagrams for software modeling.












