Now Reading: Case Study: UML State Machine Diagram for a Vending Machine System – Using PlantUML & Visual Paradigm AI to Model Real-World Behavior
-
01
Case Study: UML State Machine Diagram for a Vending Machine System – Using PlantUML & Visual Paradigm AI to Model Real-World Behavior
Case Study: UML State Machine Diagram for a Vending Machine System – Using PlantUML & Visual Paradigm AI to Model Real-World Behavior
📌 Overview
This case study explores the design and modeling of a vending machine using a UML State Machine Diagram. The system allows users to insert coins, select items, receive change, or cancel selections. The state machine captures the dynamic behavior of the vending machine across various states and transitions, making it ideal for modeling real-time and event-driven systems.
The example uses PlantUML for visualization and demonstrates how Visual Paradigm’s AI-powered state diagram generator can accelerate and simplify the modeling process.
🧩 Key Concepts in UML State Machine Diagrams
PlantUML State Machine Diagram
@startuml
skinparam {
‘ Overall style
‘ Colors
ArrowColor #333333
ArrowFontColor #333333
BackgroundColor #FFFFFF
BorderColor #333333
‘ State styling
State {
BorderColor #005073
BackgroundColor #E6F5FF
FontColor #005073
}
}
[*] –> Idle
Idle –> InsertCoin : insert_coin()
InsertCoin –> WaitingForSelection : select_item()
state “Waiting for Selection” as Selection {
WaitingForSelection –> SelectItem : choose_item()
SelectItem –> Dispense : confirm_selection()
SelectItem –> Refund : cancel_selection()
}
Dispense –> Shipped : dispense_item()
Shipped –> [*]
Refund –> Idle : return_money()
InsertCoin –> Error : invalid_coin()
Error –> [*]
@enduml
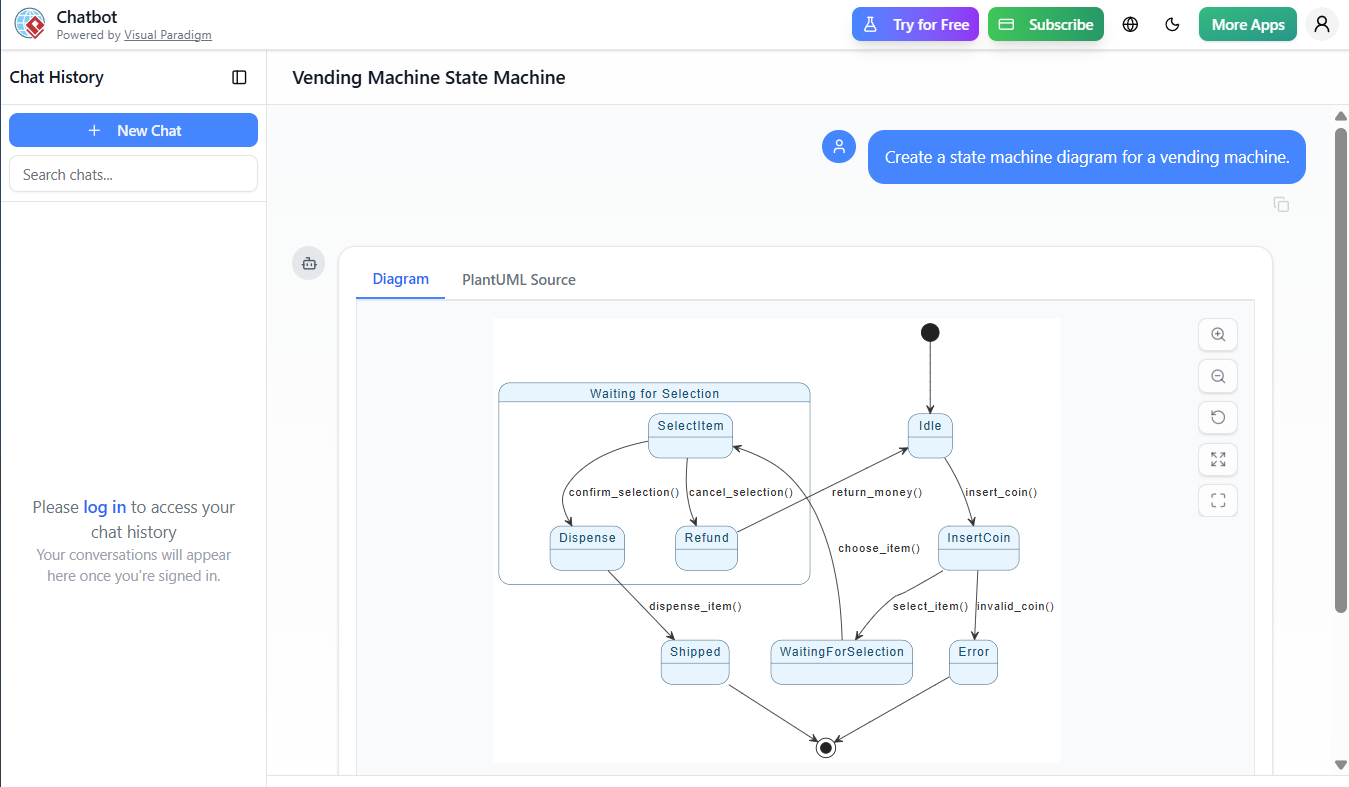
1. States
-
Represent the condition or situation of a system at a given time.
-
In our example:
-
Idle: No user interaction. -
InsertCoin: User has inserted a coin. -
WaitingForSelection: User can choose an item. -
SelectItem: Item selected, awaiting confirmation. -
Dispense: Item is being dispensed. -
Shipped: Item delivered. -
Refund: User cancels; money returned. -
Error: Invalid coin inserted.
-
✅ Tip: Use clear, descriptive names (e.g.,
WaitingForSelection, notS2) for better readability.
2. Transitions
-
Represent changes from one state to another triggered by events, guards, and actions.
-
Example:
InsertCoin --> WaitingForSelection : select_item()-
Event:
select_item() -
Action: Transition occurs when the user selects an item.
-
✅ Tip: Always include events (like
insert_coin()) and actions (likereturn_money()) to make the diagram actionable and traceable.
3. Initial and Final States
-
[*]marks the initial state — where the machine starts. -
[*]also marks the final state — where the machine returns after completing a transaction.
✅ Best Practice: Always define an initial state (
[*] --> Idle) and a final state (Shipped --> [*]), ensuring the system can be reset.
4. Composite States (Substates)
-
WaitingForSelectionis a composite state containingSelectItemandRefund. -
This allows hierarchical modeling — useful for complex behaviors.
✅ Tip: Use
state "..." { ... }blocks to group related substates and improve readability.
5. History States (Optional)
-
Not shown in this example, but useful when a system needs to resume from the last active substate after an external event.
🔧 Advanced Tip: Use
[*] --> Historyfor shallow history,[*] --> DeepHistoryfor deep history.
6. Self-Transitions & Guard Conditions
-
Not explicitly shown, but could be added:
InsertCoin --> InsertCoin : invalid_coin() [guard: coin_value < 5] -
Guards are conditions that must be true for a transition to occur.
✅ Best Practice: Use guards to prevent invalid transitions (e.g., invalid coin).
🛠️ Guidelines for Writing Effective State Machine Diagrams
| Guideline | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Start with the initial state | Always begin with [*] |
| Use meaningful state names | e.g., WaitingForSelection, not S1 |
| Keep transitions simple and focused | One event per transition |
| Avoid crossing lines | Use spatial layout (e.g., top-down or circular) |
| Group related states | Use state blocks for hierarchy |
| Use actions and events | select_item() is clearer than just “select” |
| Minimize redundant states | Avoid “state explosion” — merge similar states |
💡 Tips & Tricks
-
Use color coding (as in PlantUML skinparam) to distinguish:
-
Active states (e.g., blue background)
-
Final states (e.g., green)
-
Error states (e.g., red)
-
-
Break complex machines into sub-machines:
-
Model
InsertCoinandSelectionas separate statecharts. -
Use hierarchical state machines to reduce complexity.
-
-
Document transitions with actions:
-
select_item()→ triggers state change and logs selection. -
dispense_item()→ action on transition toDispense.
-
-
Validate with test cases:
-
Simulate user flows: insert coin → select → dispense → idle.
-
Test error paths: invalid coin → error → reset.
-
-
Use UML notation correctly:
-
Arrows:
--->for transitions. -
Dashed lines: for internal transitions (e.g.,
on_entry: reset_timer()).
-
🤖 How Visual Paradigm’s AI State Diagram Generator Helps
Visual Paradigm’s AI State Diagram Generator revolutionizes how developers and analysts create UML state machine diagrams — especially for complex systems.
✅ Key Features & Benefits:
| Feature | How It Helps |
|---|---|
| Natural Language Input | You can type: “Model a vending machine where users insert coins, select items, and receive change.” → AI generates a complete state machine. |
| Auto-generates States & Transitions | Eliminates manual trial-and-error; AI infers states like InsertCoin, WaitingForSelection, Dispense, etc. |
| Smart Event & Action Detection | Identifies events (select_item(), insert_coin()) and actions (return_money()) automatically. |
| Supports Hierarchical Modeling | AI groups states into composite regions (e.g., WaitingForSelection → SelectItem, Refund). |
| Exports to PlantUML / UML/XML | Generate code-ready diagrams with one click. |
| Real-time Validation | Flags missing transitions, unreachable states, or circular logic. |
| Integration with IDEs | Use with VS Code, IntelliJ, or Eclipse via plugins. |
🎯 Example Workflow in Visual Paradigm:
Open AI State Diagram Generator.
Type: “A vending machine that accepts coins, allows item selection, dispenses items, and returns money on cancel.”
AI generates a complete UML state machine with transitions, states, and actions.
Export as PlantUML, PNG, or XMI.
Integrate into documentation, code, or testing frameworks.
🔍 Real-World Applications
-
Embedded Systems: Car infotainment, medical devices.
-
User Interfaces: Mobile apps with complex navigation (e.g., login → OTP → home).
-
IoT Devices: Smart locks, thermostats, sensors.
-
Business Process Automation: Order fulfillment, payment processing.
📌 Why UML State Machines? They’re predictable, testable, and scalable — ideal for systems where behavior depends on sequence of events.
✅ Summary
| Element | Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Start | With [*] and define Idle as initial state |
| Transitions | Use clear events (select_item()) and actions |
| Structure | Use state blocks for hierarchy |
| Validation | Ensure no unreachable states or loops |
| Tooling | Use Visual Paradigm AI to generate fast, accurate diagrams from natural language |
📎 Final Thoughts
Your PlantUML example is a solid foundation for modeling real-world systems. By applying UML state machine best practices, using clear naming, and leveraging AI tools like Visual Paradigm, you can:
-
Accelerate design
-
Reduce errors
-
Improve collaboration
-
Enable traceability from model to code
🌟 Pro Tip: Use the AI generator to prototype, then refine with your team — it’s like having a co-pilot for system design.
📂 Resources
-
Mastering State Diagrams with Visual Paradigm AI: A Guide for Automated Toll Systems: This guide demonstrates how to use AI-enhanced state diagrams to model and automate complex behavior in software for automated systems.
-
Definitive Guide to UML State Machine Diagrams with AI: A detailed technical guide on using AI-powered tools to model dynamic object behavior using UML state machine diagrams.
-
Visual Paradigm AI Chatbot – Intelligent Diagram Generation: This resource explains how the AI chatbot, a cloud-based feature, enables users to generate diagrams instantly from their desktop software using natural language.
-
Interactive State Machine Diagram Tool: An online UML tool that supports creating, editing, and exporting detailed state machine diagrams through an interactive interface.
-
State Diagram Quick Tutorial: Master UML State Machines in Minutes: A beginner-friendly resource designed to help users quickly master core concepts and practical modeling techniques within Visual Paradigm.
-
What is a State Machine Diagram? A Comprehensive Guide to UML State Diagrams: An in-depth explanation covering the purpose, components, and real-world applications of state machine diagrams in software engineering.
-
Visualizing System Behavior: A Practical Guide to State Diagrams with Examples: A guide that highlights how state diagrams help designers identify and address potential issues early in the design process through visualization.
-
Generating Source Code from State Machines in Visual Paradigm: This technical guide provides instructions on automatically producing code from state machine diagrams to implement complex, state-driven logic efficiently.
-
How to Create a State Machine Diagram in Visual Paradigm: A step-by-step user guide detailing how to use intuitive tools to build accurate behavioral models.
-
AI Chatbot for Diagram and Model Generation: Part of the AI Toolbox, this application allows users to transform simple text prompts into complete, presentation-ready diagrams in seconds.
-
UML 2.5 Specification (ISO/IEC 19501)
Let this case study be your blueprint for mastering UML state machine diagrams — from concept to code, powered by AI and best practices.
🚀 Model with clarity. Design with intelligence. Build with confidence.












