Now Reading: AI-Powered Sequence Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide to Modeling Software Updates
-
01
AI-Powered Sequence Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide to Modeling Software Updates
AI-Powered Sequence Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide to Modeling Software Updates
Introduction: The Evolution of Visual Modeling in Software Development
In the intricate world of software engineering, the sequence diagram stands as a critical tool for visualizing the temporal flow of messages between system components. These diagrams are indispensable for mapping out complex processes, such as the downloading and installing of software updates. However, the traditional method of manually constructing these models is often fraught with challenges. It can be time-consuming and susceptible to human error, particularly when designers fail to account for edge cases like server timeouts or data validation errors.
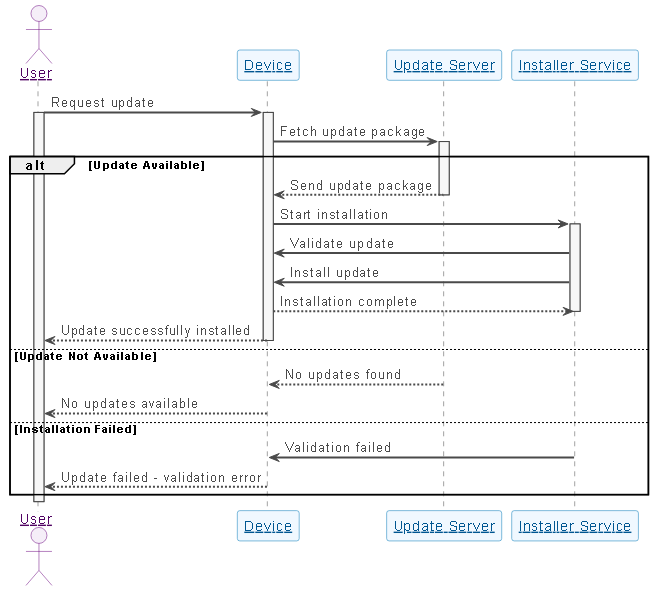
Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot represents a paradigm shift in this domain. By leveraging advanced natural language processing, it transforms the modeling process from a manual drafting task into a dynamic, conversational experience. This guide explores how AI-driven sequence diagrams allow architects and developers to model software update workflows with unprecedented precision, resilience, and speed.\
From Prompt to Precision: The Conversational Approach
Initiating the Model
The journey to a comprehensive diagram begins with a simple natural language request. In the context of a software update workflow, a user might input a prompt such as: “Create a sequence diagram describing how a software update is downloaded and installed on a device.”
Within moments, the AI interprets the semantic intent of the request and generates a fully rendered UML sequence diagram. This initial output includes the core participants necessary for the operation:
- User: The entity initiating the request, whether a human end-user or an automated trigger.
- Device: The local hardware coordinating the communication.
- Update Server: The remote repository providing the package.
- Installer Service: The internal component responsible for validation and execution.
Interactive Refinement and Edge Cases
The true capability of AI-assisted modeling is revealed during the refinement phase. Static diagrams often present the “happy path”—the scenario where everything works perfectly. However, robust software design demands resilience against failure. Through interactive dialogue, users can challenge the model with complex scenarios, such as asking, “What happens if the update server is unreachable during the download process?”
Rather than simply appending a generic error note, the AI contextualizes the failure with technical specificity. It introduces mechanisms like timeout thresholds (e.g., 30-second connection attempts) and fallback protocols (e.g., retry logic or switching to mirror servers). Visually, this is represented by introducing ‘alt’ (alternative) fragments into the sequence diagram, clearly demarcating the logic flow between a successful download and a connection failure.
Decoding the Diagram: Logic and Key Elements
To understand the value of these AI-generated models, it is essential to break down the technical elements they produce. A robust sequence diagram provides more than just a picture; it provides a blueprint for implementation.
Core Participants and Roles
The AI automatically identifies and assigns roles to the necessary components:
| Actor/Component | Role Description |
|---|---|
| User | Initiates the update request. |
| Device | Acts as the primary bridge between the user interface and the backend infrastructure. |
| Update Server | Stores the update packages and signals availability or failure. |
| Installer Service | Executes the installation while ensuring file integrity and security validation. |
Visualizing Conditional Logic
Complex decision-making is modeled using ‘alt’ blocks, which allow developers to visualize mutually exclusive scenarios:
- Update Available: The server confirms the package exists, and the flow proceeds to download and installation.
- Server Unreachable: Network issues trigger a timeout. The diagram visualizes the feedback loop, showing error messages or retry prompts sent back to the user.
- Validation Failed: If a downloaded package is corrupted or incompatible, the Installer Service rejects it, preventing potential system instability.
The AI as a Technical Consultant
Beyond drawing, Visual Paradigm’s AI acts as an interactive consultant. It possesses the ability to explain the architectural reasoning behind the diagram elements. If a user queries the logic of a retry mechanism, the AI can explain the use of exponential backoff strategies to prevent server overload.
This capability supports a wide array of modeling standards, ensuring that the tool fits into various architectural frameworks:
- ArchiMate: For high-level enterprise architecture planning.
- SysML: For systems engineering and hardware-software integration.
- C4 Model: For visualizing software architecture at different levels of abstraction.
Comparing Traditional vs. AI-Assisted Modeling
Adopting AI for sequence diagrams offers distinct advantages over traditional drag-and-drop tools:
| Feature | Traditional Tools | Visual Paradigm AI |
|---|---|---|
| Speed of Creation | Manual and time-intensive | Instant generation from text |
| Technical Accuracy | Dependent entirely on user knowledge | Standards-compliant and context-aware |
| Edge-Case Management | Often overlooked or tedious to draw | Explicitly suggested and modeled |
| Workflow | Static drafting | Interactive, conversational refinement |
Conclusion: Designing with Confidence
The integration of AI into the modeling process eliminates guesswork and reduces the cognitive load on software architects. By combining natural language processing with rigorous UML standards, Visual Paradigm’s AI Chatbot empowers teams to model complex workflows, such as software updates, with confidence. It ensures that critical aspects like resilience, error handling, and component interaction are not just imagined but explicitly visualized and documented. for teams striving to enhance their DevOps and architectural practices, AI-powered sequence diagrams represent a significant leap forward in efficiency and clarity.












